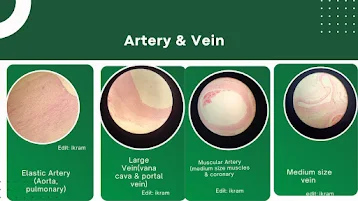
Comparison Between Histology Slides: Elastic Artery (Aorta & Pulmonary), Large Vein (Vena Cava & Portal Vein), Medium-Sized Muscular Artery (Muscle Branches & Coronary Artery), and Medium-Sized Vein
Elastic Artery ( Aorta) & Large Vein ( Vena Cava)
Medium Size Artery (Muscular) & Vein
Small Size Artery & Vein
Artery & Vein
Large Vein ( Vena Cava & Portal)
Elastic Artery( Aorta & Pulmonary)
Muscular Artery & Vein
(Medium Size)
1. Elastic Artery (Aorta & Pulmonary Artery)
Layers:
Tunica Intima:
Structure: The innermost layer, consisting of a single layer of endothelial cells sitting on a thin basement membrane.
Function: Provides a smooth lining to minimize friction as blood flows through the vessel.
Subendothelial Layer: Contains connective tissue and some smooth muscle cells.
Tunica Media:
Structure: The thickest layer in elastic arteries, composed mainly of elastic fibers arranged in concentric layers, interspersed with smooth muscle cells.
Function: Allows the vessel to stretch and recoil, helping to maintain continuous blood flow during the cardiac cycle.
Key Features: The presence of numerous elastic laminae, which distinguish elastic arteries from other types of blood vessels.
Tunica Adventitia:
Structure: Composed of connective tissue with collagen and elastic fibers, vasa vasorum (small blood vessels), and nerves.
Function: Provides structural support and nourishes the outer part of the vessel wall through vasa vasorum.
2. Large Vein (Vena Cava & Portal Vein)
Layers:
Tunica Intima:
Structure: Similar to arteries, it has a single layer of endothelial cells on a basement membrane.
Function: Ensures a smooth passage of blood with minimal resistance.
Subendothelial Layer: Thinner compared to arteries, with less connective tissue and smooth muscle.
Tunica Media:
Structure: Relatively thin compared to the tunica media of arteries, with fewer smooth muscle cells and more connective tissue. The elastic fibers are not as abundant as in arteries.
Function: Provides limited contractility, enough to maintain venous tone, but is mainly supported by surrounding skeletal muscles for blood flow.
Tunica Adventitia:
Structure: The thickest layer in large veins, consisting of connective tissue with collagen fibers, and may contain smooth muscle cells arranged longitudinally.
Function: Provides structural support and prevents the vein from collapsing. The adventitia is thicker than in arteries and often contains vasa vasorum.
3. Medium-Sized Muscular Artery (Muscle Branches & Coronary Artery)
Layers:
Tunica Intima:
Structure: Consists of endothelial cells, a basement membrane, and a thin subendothelial layer of connective tissue.
Function: Provides a barrier between the blood and the rest of the vessel wall.
Internal Elastic Lamina: A prominent, wavy elastic layer that separates the tunica intima from the tunica media.
Tunica Media:
Structure: Dominated by smooth muscle cells arranged in concentric layers, with fewer elastic fibers compared to elastic arteries.
Function: Allows for regulation of blood vessel diameter, controlling blood flow and pressure.
Key Features: The thickness of the tunica media is proportional to the vessel's role in regulating blood flow.
Tunica Adventitia:
Structure: Made up of connective tissue with collagen and elastic fibers, merging with the surrounding connective tissue.
Function: Provides structural support and may contain nerves and vasa vasorum in larger muscular arteries.
4. Medium-Sized Vein
Layers:
Tunica Intima:
Structure: Composed of a single layer of endothelial cells on a basement membrane, with a thinner subendothelial layer compared to arteries.
Function: Maintains a smooth surface for blood flow with minimal resistance.
Tunica Media:
Structure: Thinner than in medium-sized arteries, with fewer layers of smooth muscle cells and some connective tissue.
Function: Contributes to venous tone and works in conjunction with skeletal muscles to facilitate blood return to the heart.
Tunica Adventitia:
Structure: The thickest layer in medium-sized veins, composed mainly of connective tissue with collagen fibers.
Function: Provides structural support and prevents the vein from collapsing. In some veins, the adventitia may contain smooth muscle cells, especially near the heart.
Summary
Elastic Arteries: Characterized by a thick tunica media with abundant elastic fibers, enabling them to stretch and recoil with the pulsatile flow of blood from the heart.
Large Veins: Have a thick tunica adventitia with collagen fibers and some smooth muscle cells, ensuring structural integrity and support for large volumes of blood returning to the heart.
Medium-Sized Muscular Arteries: Possess a prominent tunica media dominated by smooth muscle cells, allowing for precise control of blood flow through vasoconstriction and vasodilation.
Medium-Sized Veins: Feature a relatively thin tunica media and a thick tunica adventitia, designed to support the vessel while relying on surrounding skeletal muscles to aid blood return to the heart.
Click Here to watch youtube Video




.jpeg)
.jpeg)

.jpeg)










0 Comments